Jurisdiction:
United States
Organ System:
Head and Neck
Funding Organizations:
- Cancer Prevention Institute of Texas, USA
- National Cancer Institute, USA
- Robert and Janice McNair Foundation, USA
- Translational Breast Cancer Research Training Program, USA
Research Organizations:
- Baylor College of Medicine, USA
- Johns Hopkins University, USA
- Washington University in St. Louis, USA
- Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, USA
- University of Michigan, USA
- Brigham Young University, USA
- Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, USA
- Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, USA
- New York University School of Medicine, USA
- Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, USA
- National Cancer Institute, USA
Principal Investigators
:- Bing Zhang
- Hui Zhang
- Daniel W. Chan
Publication:
External Links:
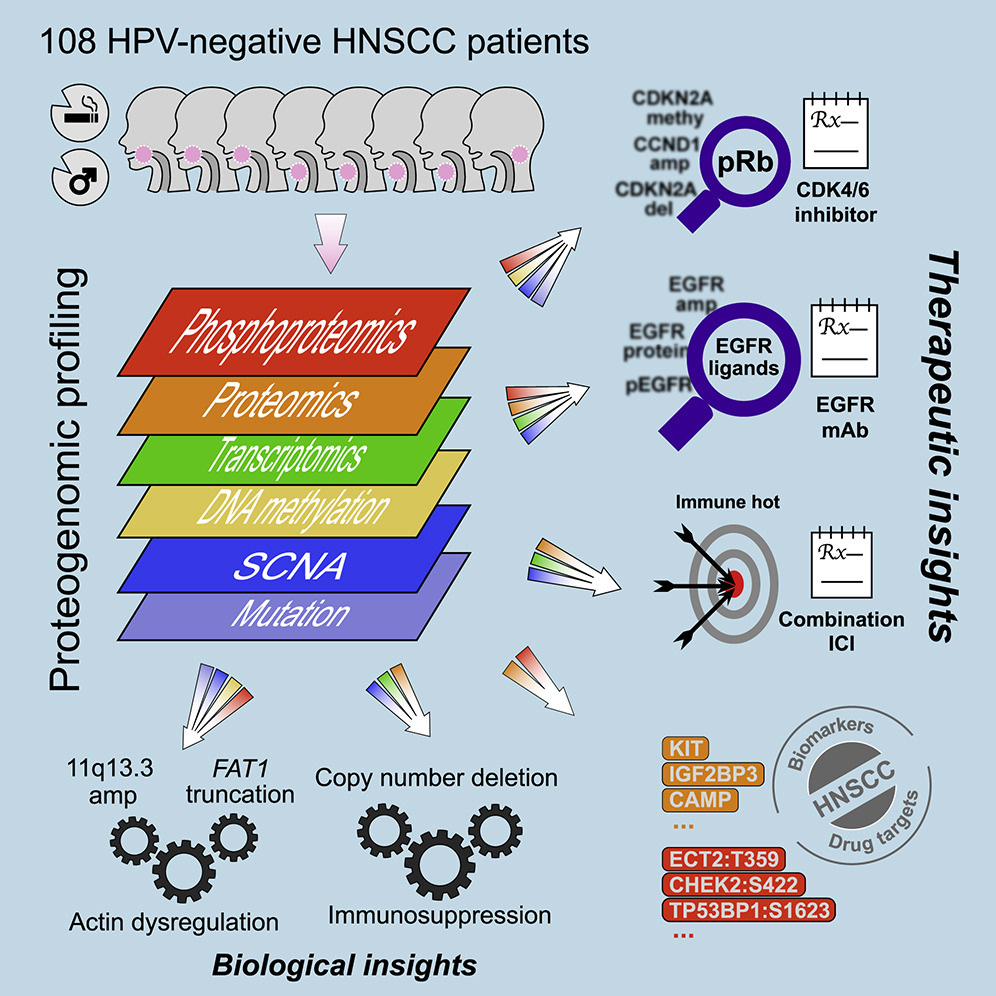
We present a proteogenomic study of 108 human papilloma virus (HPV)-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs). Proteomic analysis systematically catalogs HNSCC-associated proteins and phosphosites, prioritizes copy number drivers, and highlights an oncogenic role for RNA processing genes. Proteomic investigation of mutual exclusivity between FAT1 truncating mutations and 11q13.3 amplifications reveals dysregulated actin dynamics as a common functional consequence. Phosphoproteomics characterizes two modes of EGFR activation, suggesting a new strategy to stratify HNSCCs based on EGFR ligand abundance for effective treatment with inhibitory EGFR monoclonal antibodies. Widespread deletion of immune modulatory genes accounts for low immune infiltration in immune-cold tumors, whereas concordant upregulation of multiple immune checkpoint proteins may underlie resistance to anti-programmed cell death protein 1 monotherapy in immune-hot tumors. Multi-omic analysis identifies three molecular subtypes with high potential for treatment with CDK inhibitors, anti-EGFR antibody therapy, and immunotherapy, respectively. Altogether, proteogenomics provides a systematic framework to inform HNSCC biology and treatment.