Jurisdiction:
United States
Organ System:
Pancreas
Funding Organizations:
- National Cancer Institute, USA
- National Institutes of Health, USA
Research Organizations:
- Johns Hopkins University, USA
- Baylor College of Medicine, USA
- Washington University in St. Louis, USA
- Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, USA
- University of Michigan, USA
- Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, USA
- University of Toronto, Canada
- University Health Network, Canada
- University of Calgary, Canada
- National Cancer Institute, USA
Principal Investigators
:- Hui Zhang
- Bing Zhang
- Li Ding
Publication:
External Links:
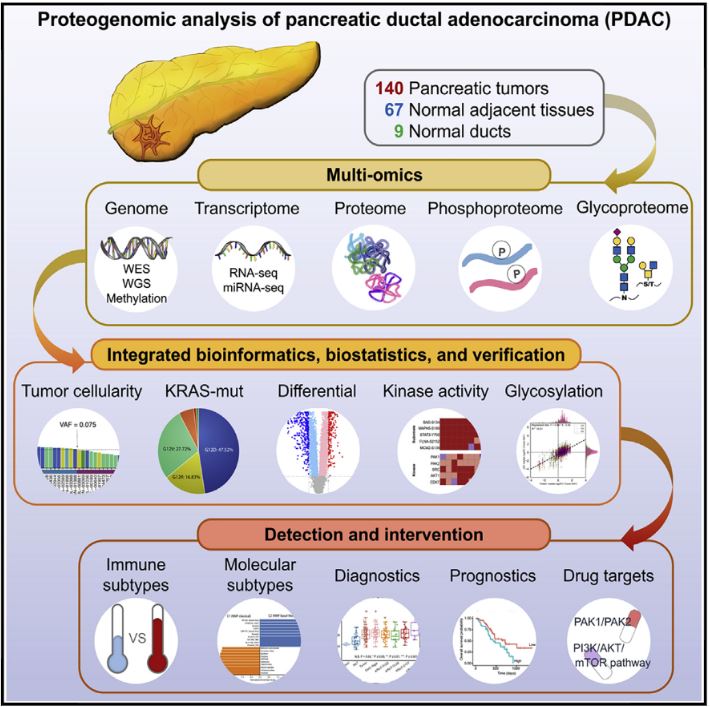
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly aggressive cancer with poor patient survival. Toward understanding the underlying molecular alterations that drive PDAC oncogenesis, we conducted comprehensive proteogenomic analysis of 140 pancreatic cancers, 67 normal adjacent tissues, and 9 normal pancreatic ductal tissues. Proteomic, phosphoproteomic, and glycoproteomic analyses were used to characterize proteins and their modifications. In addition, whole-genome sequencing, whole-exome sequencing, methylation, RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), and microRNA sequencing (miRNA-seq) were performed on the same tissues to facilitate an integrated proteogenomic analysis and determine the impact of genomic alterations on protein expression, signaling pathways, and post-translational modifications. To ensure robust downstream analyses, tumor neoplastic cellularity was assessed via multiple orthogonal strategies using molecular features and verified via pathological estimation of tumor cellularity based on histological review. This integrated proteogenomic characterization of PDAC will serve as a valuable resource for the community, paving the way for early detection and identification of novel therapeutic targets.