Jurisdiction:
South Korea
Organ System:
Pancreas
Funding Organizations:
- National Research Foundation of Korea
- Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), S. Korea
- Creative Research Initiative Program, S. Korea
Research Organizations:
- Korea University, S. Korea
- Seoul National University, S. Korea
- Ajou University, S. Korea
Principal Investigators
:- Sang-Won Lee
- Daehee Hwang
- Jin-Young Jang
Publication:
External Links:
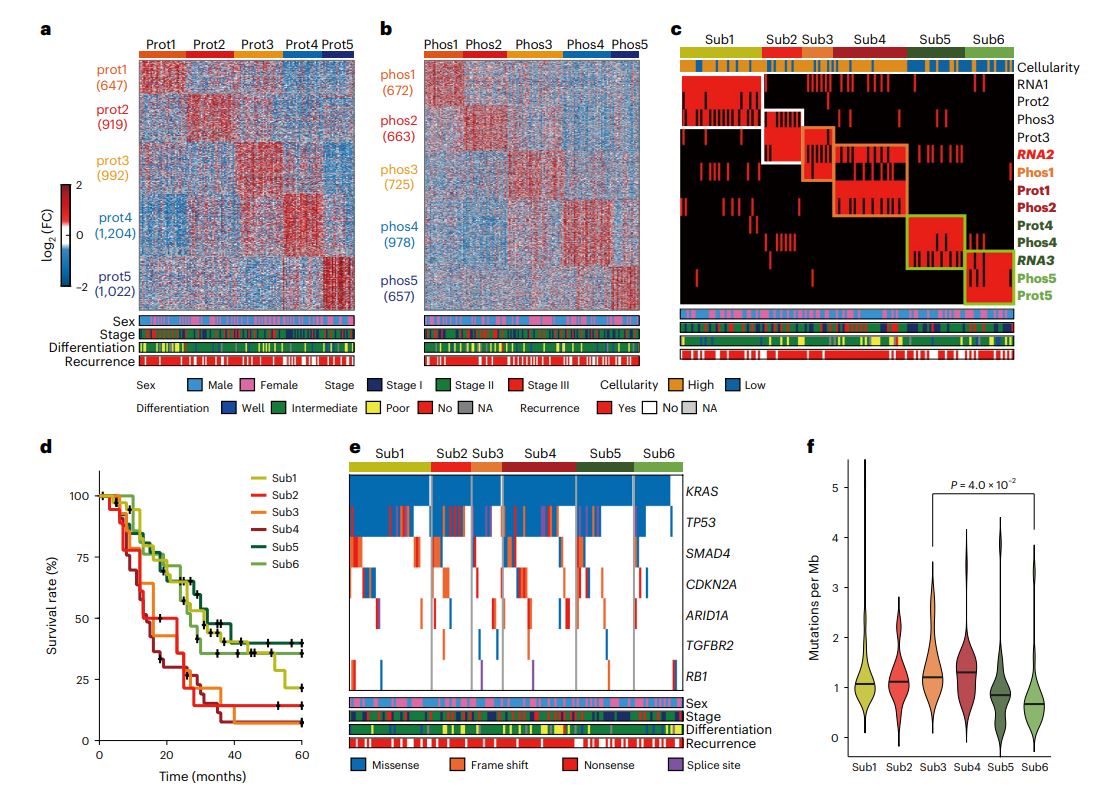
We report a proteogenomic analysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Mutation-phosphorylation correlations identified signaling pathways associated with somatic mutations in significantly mutated genes. Messenger RNA-protein abundance correlations revealed potential prognostic biomarkers correlated with patient survival. Integrated clustering of mRNA, protein and phosphorylation data identified six PDAC subtypes. Cellular pathways represented by mRNA and protein signatures, defining the subtypes and compositions of cell types in the subtypes, characterized them as classical progenitor (TS1), squamous (TS2-4), immunogenic progenitor (IS1) and exocrine-like (IS2) subtypes. Compared with the mRNA data, protein and phosphorylation data further classified the squamous subtypes into activated stroma-enriched (TS2), invasive (TS3) and invasive-proliferative (TS4) squamous subtypes. Orthotopic mouse PDAC models revealed a higher number of pro-tumorigenic immune cells in TS4, inhibiting T cell proliferation. Our proteogenomic analysis provides significantly mutated genes/biomarkers, cellular pathways and cell types as potential therapeutic targets to improve stratification of patients with PDAC.